Understanding the New FCEN Corporate Transparency Act
The New FCEN Corporate Transparency Act marks a significant shift in the regulatory landscape aimed at increasing corporate transparency in the United States. This legislation reflects the government's commitment to curbing illicit financial practices and strengthening corporate accountability. In this introductory section, we will provide an overview of the Act and its essential components, setting the stage for a more detailed examination in subsequent sections.
Key Takeaways
The FCEN Corporate Transparency Act is a pivotal regulatory advancement that enforces increased corporate transparency and accountability.
It was enacted to combat issues such as tax evasion, fraud, and money laundering by imposing new reporting requirements on businesses.
Defining beneficial ownership and understanding the criteria outlined by the Act are critical for businesses to comply with the new regulations.
The Beneficial Ownership Registry will collect, store, and utilize beneficial ownership information to promote transparency and hinder illegal financial practices.
Businesses must adapt and collaborate with regulatory agencies, like FCEN, to ensure compliance and foster ethical business practices.
Exploring the Purpose of the FCEN's Corporate Transparency Act
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FCEN) introduced the Corporate Transparency Act with the aim of addressing the limitations in the current financial transparency landscape. The Act serves as a response to the pressing need for better financial transparency within corporate entities. This section will delve into the underlying motives of the Act and explore how it aims to enhance financial transparency, promote anti-corruption measures, and combat money laundering within today's corporate environment.
The Drive for Enhanced Financial Transparency
At the heart of the Corporate Transparency Act is the objective of providing clearer insight into the financial activities of American businesses. Existing corporate transparency requirements have proven insufficient in countering issues such as deliberate tax evasion, fraud, and the concealment of illicit funds through opaque corporate structures. The FCEN agenda seeks to address these problems by mandating the disclosure of beneficial ownership information and improving the overall transparency of corporate financial activities.
Through the implementation of stronger corporate transparency requirements, the Act strives to:
Expose hidden financial activities and connections
Prevent the misuse of corporate structures for illicit financial activities
Facilitate investigation and enforcement actions by regulatory agencies
Boost investor confidence through greater accountability and disclosure
Anti-Corruption and Combating Money Laundering Objectives
One of the core objectives of the Corporate Transparency Act is to deter corruption and money laundering activities. The increased transparency brought about by the Act will hinder illegal financial practices perpetrated through the concealment of true owners and other nefarious mechanisms. It strives to mitigate corrupt practices and make it more challenging for illicit actors to take advantage of corporate structures for their gain.
"The Corporate Transparency Act aims to interrupt the ability of criminals and other illicit actors to use anonymous shell companies by requiring the reporting of the true beneficial owners of newly formed and existing companies." – FCEN
The Act establishes a range of anti-corruption and anti-money laundering measures, including:
Requirement for new and existing companies to report beneficial ownership information to the FCEN
Creation of a Beneficial Ownership Registry to centralize and store ownership data
Better coordination between financial institutions, regulators, and law enforcement agencies
Stiffer penalties for non-compliance and falsification of information
By enhancing financial transparency and focusing on the key areas of anti-corruption and combating money laundering, the Corporate Transparency Act is poised to make a significant positive impact on the corporate landscape and establish more transparent corporate structures for the benefit of businesses and society at large.
The Impact of the New FCEN Regulations on Businesses
The new regulations introduced by the FCEN have caught the attention of businesses across various industries due to their far-reaching implications on corporate governance and business regulatory compliance. This section delves into the challenges and opportunities presented by these regulations, analyzing their impact on maintaining compliance and promoting ethical business practices.
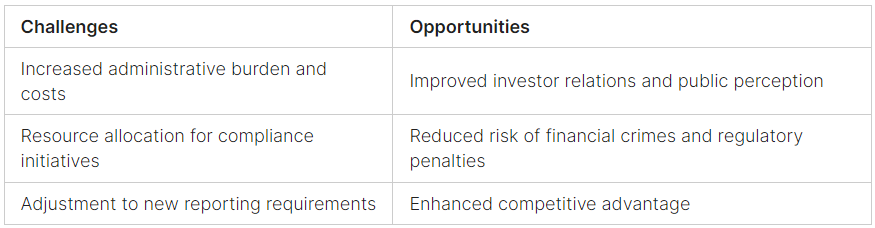
Challenges: Adhering to the FCEN regulations comes with its own set of unique challenges. Foremost among them is the need for businesses to invest in updating their internal processes and systems to meet the compliance requirements, which often involve increased administrative burdens and costs.
For many businesses, implementing the necessary changes to comply with these new regulations will be a substantial undertaking, necessitating the allocation of considerable resources, both human and financial.
Opportunities: Despite the obstacles, the adoption of the new FCEN regulations also presents businesses with opportunities to enhance their corporate governance and risk management capabilities. The increased transparency and accountability requirements can lead to improved business ethics and foster a company culture centered on trust and integrity.
Improved investor relations and public perception: Companies that can demonstrate a strong commitment to corporate transparency will likely earn the trust of investors and the public, ultimately improving their reputation and making them more attractive to potential shareholders.
Reduced risk of financial crimes and regulatory penalties: By increasing transparency and accountability, businesses can minimize the risks of financial crime, such as money laundering and fraud, while also reducing the likelihood of incurring penalties for non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
Enhanced competitive advantage: Companies that adapt quickly to the new regulatory landscape and seize the opportunities to optimize their practices can garner a competitive advantage over those that struggle to adapt.
In conclusion, the FCEN regulations impact on businesses will be felt across various industries, as they grapple with both the challenges and opportunities of compliance. By adapting to these new requirements, companies can work towards creating a more transparent and accountable corporate environment, which ultimately benefits their reputation and bottom line.
Defining Beneficial Ownership Under the Corporate Transparency Act
The Corporate Transparency Act, part of the New FCEN regulations, provides a set of criteria to identify beneficial owners of companies, aiming to unmask the true controllers of corporate entities. The Act outlines the requirements for defining beneficial ownership, ownership identification, and FCEN ownership guidelines. This section explores these criteria, as well as the effects of applying these new standards across business operations, beneficial owner reporting, and corporate structure implications.
Criteria for Identifying Beneficial Owners
The Act defines a beneficial owner as any individual who, directly or indirectly:
Exercises substantial control over a corporation or limited liability company (LLC).
Owns 25% or more of an ownership interest in the entity.
Receives substantial economic benefits from the assets of the corporation or LLC.
This definition includes both domestic and foreign individuals. The beneficial ownership identification process requires companies to provide the following information on each beneficial owner:
Full legal name.
Date of birth.
Current residential or business address.
A unique identifying number from an acceptable identification document, such as a passport or driver's license.
The FCEN ownership guidelines ensure that companies can no longer hide behind complex corporate structures and must report their true controllers, contributing to transparency and combating money laundering, tax evasion, and other illegal activities.
Implications for Business Operations
Defining beneficial ownership has notable implications for business operations, as corporations and LLCs are subject to increased reporting responsibilities and may need to make operational changes to remain in compliance. Some of these impacts include:
Additional reporting requirements: Companies must submit their beneficial owner information at the time of incorporation, and any changes in ownership must be updated within one year. The need for accurate and timely reporting may necessitate the hiring of compliance officers or implementing new tracking systems to manage these responsibilities.
Changes to corporate structures: To adhere to the new regulations, some businesses may need to reevaluate their corporate structures and ownership arrangements. This could include reassessing anonymous ownership and shell company usage, as well as enhancing due diligence measures to ensure accurate ownership information.
Overall, the Corporate Transparency Act aims to make it difficult for individuals to hide behind anonymous corporate structures by standardizing the beneficial ownership criteria and increasing the transparency of business operations. While these changes may present challenges, they are a significant step in combating illegal financial activities while promoting a more accountable and transparent business landscape.
Requirements and Deadlines for Compliance
Adhering to the new compliance requirements stipulated under the Corporate Transparency Act is of utmost importance for companies looking to remain on the right side of the law. Ensuring timely and accurate submissions of required information will allow businesses to maintain their standing with regulatory agencies while also contributing to the fight against money laundering and other illicit activities.
There are several deadlines and specific requirements that companies need to adhere to under the new FCEN regulations. These can be broadly categorized into reporting requirements, record-keeping, and beneficial ownership identification requirements.
Strict adherence to these regulatory compliance requirements is crucial in order to avoid potential penalties and legal repercussions. Companies should take proactive steps to ensure they are fully compliant as the FCEN reporting deadlines approach.
In order to maintain good standing and remain compliant, it is important for companies to invest the necessary time and resources to effectively implement the measures outlined under the Corporate Transparency Act.
To assist in these efforts, companies may want to consider the following best practices:
Developing a comprehensive compliance program;
Providing regular training for staff responsible for reporting and record-keeping;
Ensuring a clear understanding of beneficial ownership criteria as detailed in the Act;
Implementing robust internal controls to prevent missed reporting deadlines;
Staying abreast of any changes to regulations and guidelines relevant to the FCEN Act.
By taking these steps, companies can effectively fulfill their obligations under the Corporate Transparency Act, demonstrating commitment to regulatory adherence and contributing to a more transparent corporate environment.
Understanding the Beneficial Ownership Registry
The Beneficial Ownership Registry, established under the FCEN's Corporate Transparency Act, serves as a centralized platform to collect, store, and utilize beneficial ownership information. Its primary purpose is to enhance transparency in corporate ownership structures, facilitate enforcement actions against financial crimes, and bolster the overall data collection efforts of the FCEN.
How the Registry Works
The ownership registry operation begins with businesses submitting their beneficial ownership information to the FCEN. Required data includes the beneficial owners' full legal names, dates of birth, addresses, and identification numbers. The registry then processes the submitted information and stores it securely for future reference and analysis by authorized parties.
With the FCEN data collection, the registry aims to build a comprehensive database of beneficial owners associated with businesses operating within the United States. This database will aid in improving oversight and preventing illicit financial activities, such as money laundering, tax evasion, and fraud.
"The Beneficial Ownership Registry is critical to shedding light on the complex corporate ownership structures that have long facilitated financial crimes."
Access and Privacy Concerns Addressed
Privacy concerns are inherently associated with the collection and storage of sensitive personal and corporate ownership data. To address these concerns and ensure protected registry access, the FCEN Act incorporates robust data protection measures.
Access to the registry's data is limited to specific entities and individuals who meet strict authorization criteria. Primarily, law enforcement agencies and regulatory authorities will have access to the Beneficial Ownership Registry to facilitate investigations. Additionally, financial institutions may seek a customer's consent to access the data for KYC (know-your-customer) and AML (anti-money laundering) compliance purposes.
Law enforcement agencies
Regulatory authorities
Financial institutions (with customer consent)
Furthermore, FCEN ensures that data protection measures are consistently reviewed and updated to account for advancements in technology, giving businesses increased confidence in the security of their sensitive information.
In summary, the Beneficial Ownership Registry strengthens the FCEN's oversight on corporate transparency while addressing privacy concerns and safeguarding sensitive data. It serves as a proactive tool that enables both domestic and global actors to take collective action against financial crimes.
Exemptions and Exceptions Within the Corporate Transparency Act
The Corporate Transparency Act aims to increase corporate transparency and combat illicit activities, such as money laundering and tax evasion. However, understanding that not all entities should be subject to the same disclosure requirements, the Act includes specific exemptions and exceptions for certain business categories. This section will outline exempted businesses and entities, offering insight into the rationale behind these exceptions and their impact on the overall efficacy of the Act.
Publicly traded companies, already subject to similar disclosure requirements under federal securities laws.
Financial institutions and credit unions,
Government and charitable organizations, subject to other transparency regulations.
Existing entities with a physical operating presence in the U.S. and over 20 full-time employees, ensuring day-to-day oversight over their activities.
Companies generating over $5 million in annual revenue, making it more challenging to conceal illegal activities.
Entities owned by exempt businesses, reducing redundant reporting requirements.
Employers with more than 20 full-time employees in the U.S., $5 million annual revenue, and an in-person operating presence are exempt. This targets shell companies formed solely to hide assets or evade taxes.
These Act exemptions, FCEN Act exceptions, and transparency act exclusions seek to balance the need for increased corporate transparency with the realities of operating businesses that are already subject to strict oversight and reporting requirements. By excluding certain entities from the scope of the Corporate Transparency Act, the legislation acknowledges existing regulatory structures and minimizes unnecessary burdens on businesses while still pursuing its primary objective of uncovering illicit activities and promoting transparency.
Navigating Corporate Accountability in the Wake of the FCEN Act
In the face of new regulatory requirements set by the FCEN Act, businesses must reevaluate their internal processes and ensure strict adherence to corporate accountability standards. This section aims to provide effective strategies and best practices for businesses looking to achieve and maintain transparency, enhancing their compliance with the FCEN Act.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance
Adopting and implementing compliance best practices can help businesses meet the new FCEN conformity requirements. By focusing on the following strategies, businesses can better navigate the waves of regulatory changes and establish a steadfast commitment to corporate accountability:
Review and update internal processes: Conduct a thorough assessment of existing processes, identifying areas that need improvement or modification to align with the Act's requirements. This includes reviewing business structures, operations, and reporting procedures to ensure full compliance.
Implement robust record-keeping systems: Maintaining accurate and comprehensive records for beneficial ownership is imperative in demonstrating transparency and compliance. Invest in secure and well-structured databases that simplify the process of information collection, storage, and retrieval.
Establish clear communication channels: Clear communication between company stakeholders, employees, and regulatory bodies is essential in fostering corporate accountability. Ensure that everyone is well-informed of the changes required by the Act and regularly update them to maintain awareness.
Engage in proactive risk management: Identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in business operations that could lead to compliance issues. Be proactive in addressing these risks and developing contingency plans to protect the organization's reputation and standing with regulators.
Invest in employee training and development: Equip your workforce with the knowledge and resources necessary to navigate the new FCEN Act requirements. Offer training programs on compliance and corporate accountability, emphasizing the importance of adhering to these standards.
Collaborate with legal and compliance experts: Consult legal and compliance experts to ensure a full understanding of the Act's requirements and its implications on business operations. Their guidance will be invaluable in developing strategies to address regulatory concerns and meet transparency goals.
By incorporating these best practices, businesses can pave the way for a successful transition in the age of the FCEN Act. Establishing a culture of corporate accountability will not only help companies meet compliance requirements but also contribute to a more transparent and ethical corporate landscape.
How the FCEN Act Enhances Transparency in Business Transactions
The introduction of the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FCEN) Corporate Transparency Act aims to significantly improve the transparency and disclosure of corporate practices across all industries. As a result, businesses will need to adapt to the changing landscape by embracing new regulatory requirements to ensure their financial dealings remain above board. In this section, we will examine the various ways the FCEN Act works to enhance transparency in business transactions, specifically through improved disclosures and tracking financial flows within and between corporations.
One of the key provisions of the FCEN Act is the requirement for companies to disclose the identities of their beneficial owners. By making this information publicly available, the Act promotes increased transparency in business transactions by shedding light on the true nature of a company's ownership structure. This enhanced visibility is particularly important in industries known for high levels of fraud and corruption, where hidden owners can manipulate operations to serve their own interests, placing legitimate businesses and partners at risk.
Furthermore, the FCEN Act's focus on transparent corporate practices will likely lead to increased due diligence efforts on the part of companies entering into partnerships or acquisitions. Given the heightened scrutiny and accountability enforced by the Act, businesses will be more likely to closely evaluate potential partners' ownership structures, ensuring that they are compliant with the new regulations.
Improved Disclosures and Reporting Requirements
Companies subject to the FCEN Act are obligated to submit beneficial ownership details and other relevant information to the federal Beneficial Ownership Registry. By gathering this data in a centralized database, the Act facilitates FCEN disclosure improvement across all businesses, increasing the information available to regulatory agencies tasked with monitoring compliance and enforcing regulations.
“The FCEN Act enables regulators to have a better understanding of corporate ownership structures, enhancing their ability to identify potential instances of fraud and money laundering.”
This increased level of transparency allows for heightened scrutiny by regulators and other stakeholders, including financial institutions and investors. Consequently, businesses that adhere to transparent corporate practices can benefit from greater trust, which can facilitate the attraction of investment and development of long-term partnerships.
Tracking Financial Flows within and between Corporations
Another significant aspect of the FCEN Act is its emphasis on tracking financial flows within and between corporations. With the increased visibility provided by the Beneficial Ownership Registry, regulators can now more effectively monitor transactions and financial activities among companies. This heightened monitoring capability makes it easier to identify patterns of suspicious behavior and potential illicit activities, such as money laundering or other financial crimes.
In conclusion, the FCEN Act presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses to improve their corporate practices in terms of enhanced transparency and disclosure. By embracing these new regulatory requirements, companies can benefit from improved trust and accountability, ultimately fostering a more stable and ethical business ecosystem.
The Role of Government Regulation in Financial Disclosure
Government regulation plays a crucial role in shaping corporate financial disclosure practices by setting the standards that businesses must adhere to, ensuring accurate and transparent financial information. These regulations aim to foster trust among the public, investors, and regulators by mitigating fraud, tax evasion, and other illegal financial activities. It is important to underscore the significance of collaboration between regulatory agencies, like the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FCEN), and businesses to ensure compliance with the new regulations and promote a fair and transparent marketplace.
Collaboration Between Agencies and Businesses
Interagency collaboration and FCEN partnership are essential elements in promoting transparency and boosting compliance with regulations. By working closely with businesses, regulatory agencies can provide guidance and assistance to help navigate the complex landscape of financial disclosure requirements. This collaborative approach fosters mutual understanding and improves the overall efficiency of the regulatory process.
“Effective regulation demands close collaboration between agencies, businesses, and stakeholders, with a shared goal of ensuring corporate financial transparency and accountability.”
Some practical steps that can be taken to enhance collaboration between businesses and regulatory agencies include:
Regularly participating in industry workshops, forums, and conferences to foster dialogue and exchange ideas.
Consulting with businesses during the drafting and implementation stages of new regulations to ensure practicality and feasibility.
Providing clear guidance and resources, such as online tools and training, to help businesses comply with financial disclosure requirements.
In addition to the collaboration between regulatory agencies and businesses, maintaining open channels of communication with other stakeholders, such as professional associations, auditing firms, and investors, can further strengthen the impact of government regulation on financial disclosure.
In conclusion, government regulation is vital in shaping corporate financial disclosure practices, promoting transparency, and reducing the risks of fraudulent activities. The interagency collaboration and FCEN partnership underscore the importance of working together to achieve these objectives, ensuring the long-term stability and success of the financial marketplace while protecting the interests of businesses and stakeholders alike.
International Implications of the FCEN Corporate Transparency Act
The FCEN Corporate Transparency Act is not only reshaping the financial regulatory landscape within the United States but also has wider international implications. It is crucial to understand its impact on international businesses and financial institutions, as well as the potential for cross-border cooperation in the pursuit of enhanced corporate transparency.
Considering the increasingly globalized nature of financial markets and commerce, the FCEN global impact extends beyond domestic entities. By imposing transparency requirements on foreign companies conducting business or owning assets in the United States, the Act directly affects international corporate structures. Additionally, as part of the global response to financial crimes and corruption, the Corporate Transparency Act aligns with efforts made in other parts of the world to promote a more transparent financial system.
Increased cross-border transparency is essential to combat financial crimes on a global scale effectively.
In order to promote international cooperation, the United States has been actively engaging with other jurisdictions to share information and work collaboratively on matters related to financial transparency and anti-money laundering. One example is the high-level collaboration between the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the U.S. Department of the Treasury to develop and implement international standards for counter-terrorist financing and anti-money laundering.
Reports on international cooperation efforts include:
Sharing beneficial ownership and financial transaction information with foreign law enforcement agencies.
Working collaboratively on the development of mutually recognized compliance frameworks.
Encouraging the adoption of corporate transparency principles similar to the FCEN Act by other countries.
With an enhanced level of cross-border transparency, many businesses may face the challenge of complying with multiple regulatory frameworks and jurisdictions. Despite these challenges, the following table showcases some anticipated benefits from the global impact of the FCEN Act:
In conclusion, the international implications of the FCEN Corporate Transparency Act are far-reaching, impacting businesses and financial institutions worldwide. Through increased cross-border transparency and international cooperation, the global financial system stands to benefit from a heightened focus on accountability, providing a more robust defense against financial crimes and promoting a more transparent marketplace.
Embracing a New Era of Corporate Transparency
In this article, we have delved into the intricacies of the newly introduced FCEN Corporate Transparency Act, exploring the crucial aspects of the regulatory changes and their impact on the American corporate landscape. The significant shift toward enhanced financial transparency and accountability driven by the FCEN is undeniable, and businesses must adapt to the compliance requirements to improve corporate governance and foster an ethical business environment.
As the new legislation ushers in a more transparent business environment, companies should be prepared to meet the challenges they may encounter, namely identifying beneficial owners and adhering to the reporting deadlines. By doing so, they are better equipped to face obstacles such as tax evasion, fraud, and money laundering while also reaping the benefits of increased corporate transparency.
Collaboration between regulatory agencies and businesses is paramount for the successful implementation of the Act. By nurturing a cooperative and communicative relationship, businesses can ensure their compliance with the FCEN regulations while adhering to the best practices that promote transparency and integrity within their organization.
The FCEN Corporate Transparency Act not only impacts the United States but also influences the global financial landscape, thus fostering cross-border transparency and fostering international cooperation in the pursuit of ethical and transparent business practices.
To conclude, adapting to the new era of corporate transparency is not only a regulatory necessity but also a strategic step toward participating in a more equitable market that promotes a level playing field for all businesses. The benefits of the FCEN regulatory summary and compliance recap shared in this article are evident, and now is the time for businesses to demonstrate their commitment to transparency and integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we address some common questions related to the Corporate Transparency Act to provide further clarity and understanding. By covering these key topics, we aim to give readers a comprehensive understanding of the Act's implications and requirements.
1. What is the primary purpose of the FCEN Corporate Transparency Act?
The main objective of the Act is to increase transparency in corporate structures and financial practices, with a focus on combating money laundering, tax evasion, and corruption. By requiring companies to disclose their true beneficial owners, the Act aims to promote corporate accountability and prevent the misuse of shell companies for illicit purposes.
2. Who needs to comply with the new FCEN regulations?
The Corporate Transparency Act applies to a broad range of businesses across different industries. While some entities are exempt due to their existing regulatory requirements (such as banks, credit unions, and publicly-traded companies), most companies will need to comply with the Act's provisions, including reporting beneficial ownership information to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
3. How does the Act define beneficial ownership, and what are the implications for businesses?
Under the Act, a beneficial owner is any individual who owns 25% or more of a company or has significant control over it. Businesses are required to file a report with FinCEN disclosing their beneficial owners' names, addresses, dates of birth, and identification numbers. This reporting requirement may have an impact on internal processes, necessitating operational adjustments for businesses to remain compliant.
4. How does the Corporate Transparency Act improve transparency in business transactions?
The Act strengthens transparency by uncovering the true ownership and control of corporations, making it harder for criminals to hide their illegal activities behind opaque corporate structures. Improved disclosures and tracking of financial flows within and between corporations should help deter tax evasion, corruption, and other fraudulent activities.
FAQ
What is the New FCEN Corporate Transparency Act?
The New FCEN Corporate Transparency Act is a piece of legislation aimed at increasing financial transparency within corporate entities in the United States. It seeks to combat issues such as tax evasion, fraud, money laundering, and corruption by requiring corporations to disclose their true beneficial ownership information.
How does the Act define beneficial ownership?
The Act defines beneficial ownership as individuals who directly or indirectly control a company, have substantial interest or ownership stake, or receive benefits from the company's assets. The goal is to unmask the true controllers of corporate entities and ensure financial transparency.
What are the requirements for businesses under the FCEN Act?
Businesses are required to report their beneficial ownership information to the Beneficial Ownership Registry, including identifying details such as name, birthdate, address, and a unique identification number. They must also keep this information up-to-date and submit it within the specified deadlines imposed by the Act.
Which businesses are exempt from the Corporate Transparency Act?
The Act provides exemptions for certain categories of businesses and entities, such as publicly traded firms, government entities, and other regulated institutions like banks and credit unions. The rationale behind these exceptions is to exclude entities that already have stringent reporting requirements or are inherently low-risk in terms of money laundering and corruption.
How does the Beneficial Ownership Registry work?
The Beneficial Ownership Registry collects, stores, and utilizes beneficial ownership information reported by businesses under the Act. Access to the registry is restricted to authorized individuals, such as law enforcement agencies and financial institutions, to protect the privacy of the disclosed information and prevent unauthorized access.
What are the best practices for ensuring compliance with the FCEN Act?
Businesses can adopt strategies such as implementing robust internal processes for collecting, verifying, and storing beneficial ownership information, providing regular training to employees on compliance requirements, and partnering with legal or compliance experts to stay up-to-date on the latest regulations.
How will the FCEN Act impact international businesses and financial institutions?
The FCEN Act will have international implications as it affects not only U.S.-based businesses but also foreign companies with a presence in the United States. This may lead to increased global cooperation in enhancing corporate transparency and combating financial crimes, as well as promoting a fair and transparent global marketplace.